WebAuthenticator
The WebAuthenticator helps you simplify OAuth workflows in your application with a simple single-line call.
First in your application constructor or in the Main program, add an OAuth startup activation check:
public App()
{
if (WebAuthenticator.CheckOAuthRedirectionActivation())
return;
this.InitializeComponent();
}
Next you can make a make a call to authenticate using your default browser:
WebAuthenticatorResult result = await WinUIEx.WebAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync(authorizeUrl, callbackUri);
Configuration
Your app must be configured for OAuth with schema activation. The scheme must be the first part of the url, ie if your oauth redirection url starts with for instance myscheme://signin/, the scheme would be myscheme. Note that http(s) schemes are not supported here.
Packaged Apps
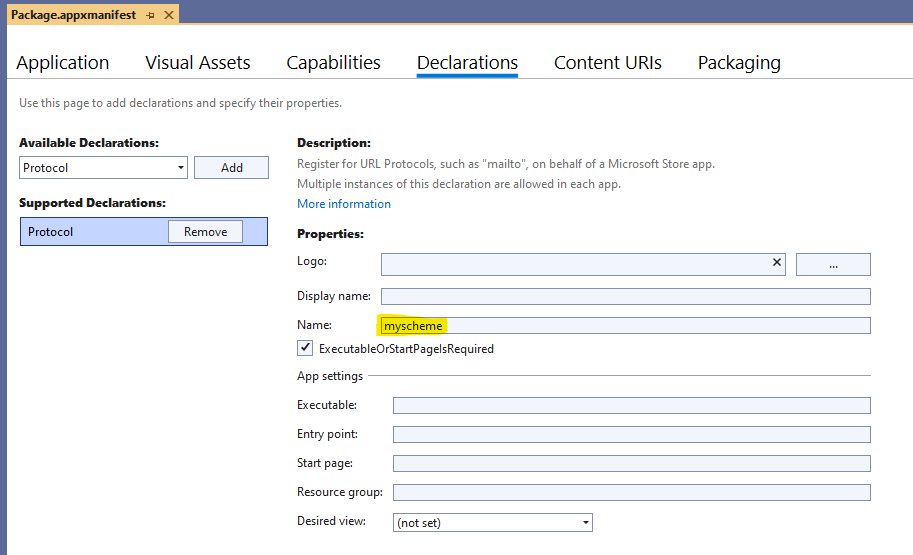
If your app is packaged, in your app's Package.appxmanifest under Declarations, add a Protocol declaration and add the scheme you registered for your application's oauth redirect url under "Name".
For example if your callback uri is "myscheme://loggedin", your manifest dialog should look like this:
Unpackaged Apps
If your app is unpackaged, instead of relying on the app manifest to handle this for you, make sure you register the application for protocol activation. For example:
try
{
Microsoft.Windows.AppLifecycle.ActivationRegistrationManager.RegisterForProtocolActivation("myscheme", "Assets\\Square150x150Logo.scale-100", "My App Name", null);
var result = await WebAuthenticator.AuthenticateAsync(authorizeUri, callbackUri, cancellationToken);
}
finally
{
Microsoft.Windows.AppLifecycle.ActivationRegistrationManager.UnregisterForProtocolActivation("myscheme", null);
}